Understanding Carbon Capture
Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS) is a method that captures carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industries and stores them underground. It requires significant energy, paradoxically leading to increased emissions. There are risks of leaks and environmental damage, and the infrastructure development can disrupt communities. CCS diverts resources from renewable energy and may not effectively address the climate crisis.
There are several types of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technologies that have been developed:
- Post-combustion capture: This method captures CO2 emissions after fossil fuels are burned to produce energy. It involves separating CO2 from flue gases using chemical solvents or other processes.
- Pre-combustion capture: This technique is used in integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) power plants. It involves converting fossil fuels into a mixture of hydrogen and CO2 before combustion. The CO2 is then captured and stored, while hydrogen is used as a fuel.
- Oxy-fuel combustion: This approach involves burning fossil fuels in pure oxygen instead of air, resulting in a flue gas primarily composed of CO2 and water vapor. The CO2 is then captured from the flue gas.
- Industrial capture: This method captures CO2 emissions from industrial processes such as cement and steel production. It involves integrating capture technologies into the industrial processes themselves to capture CO2 before it is released into the atmosphere.
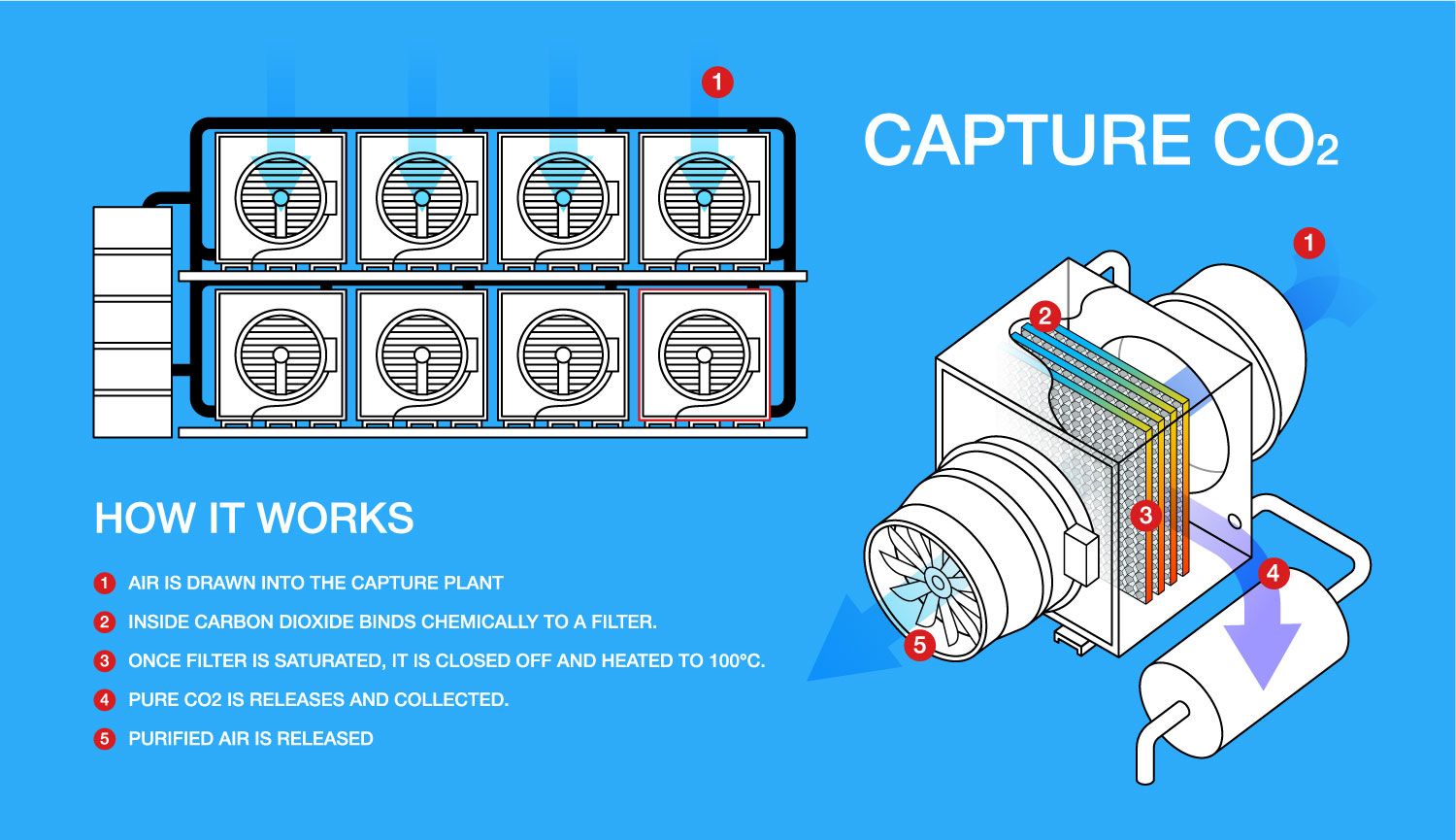
- Direct air capture (DAC): DAC technology aims to remove CO2 directly from the ambient air. It uses chemical processes or sorbents to capture CO2 from the surrounding air. The captured CO2 can then be stored or utilized.
It’s important to note that while these technologies exist, their effectiveness, scalability, and environmental impact vary. Additionally, the deployment of CCS on a large scale faces economic and logistical challenges, making it a controversial solution to address carbon emissions.